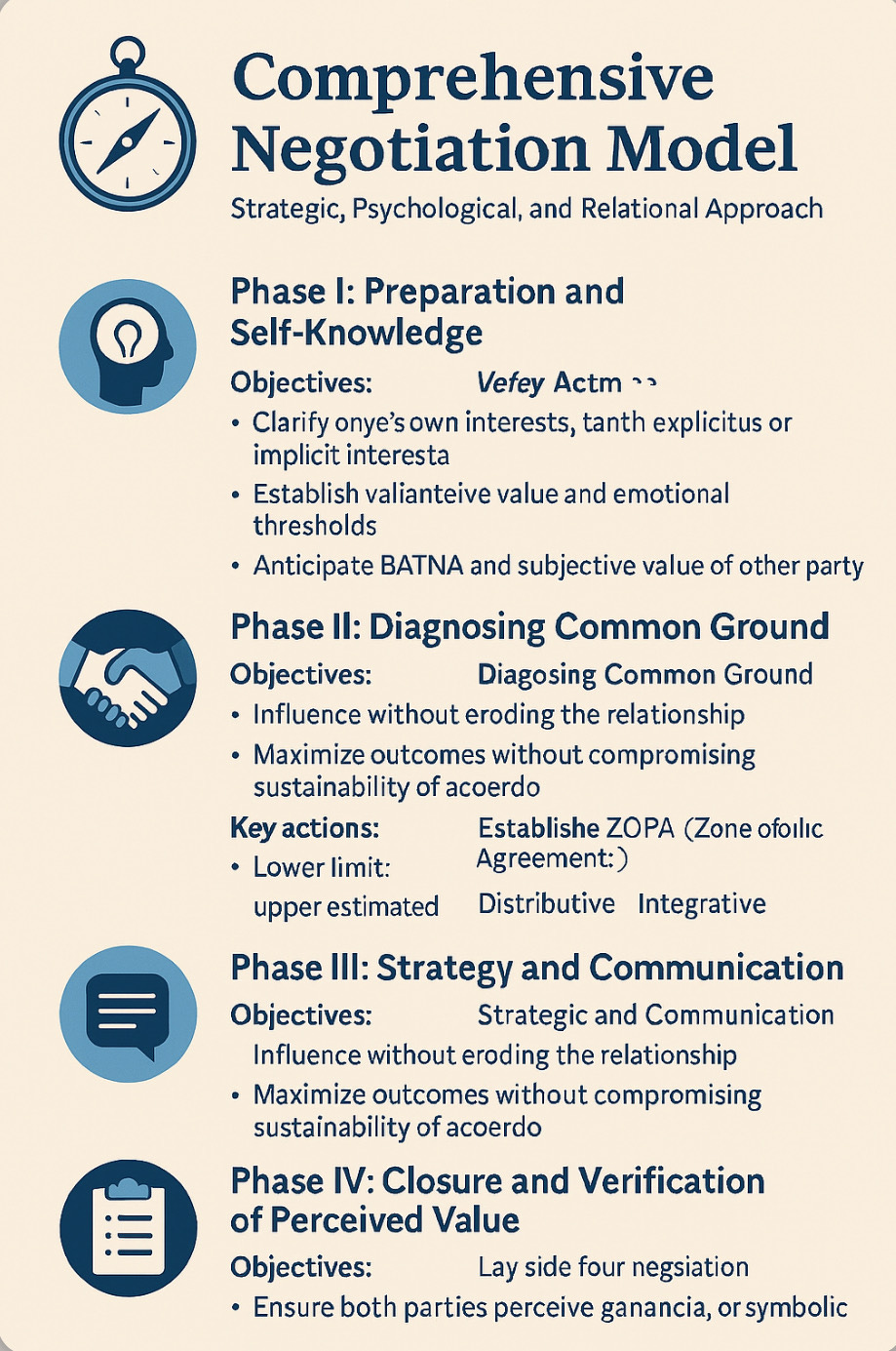
🧭 Comprehensive Negotiation Model. Part II
Everyday Applications of Game Theory
1. Personal and Workplace Negotiations
• When discussing a salary increase, deciding whether to accept an offer, or negotiating conditions, we often use strategies akin to Nash equilibrium: seeking a point where neither party has an incentive to change their decision unilaterally.
• Example: If you know your employer cannot offer a higher salary, you might negotiate non-monetary benefits (flexibility, recognition), thereby creating integrative value.
2. Interpersonal Relationships
• In couples, friendships, or families, many decisions are interdependent: should I yield or insist? cooperate or protect myself? Game theory helps us understand when cooperation is beneficial and when boundaries must be set.
• Example: In an argument, if both parties insist on being right, the result is mutual loss. If one yields strategically, it may open space for resolution.
3. Consumer Behavior and Market Dynamics
• Choosing between brands, deciding when to buy, or responding to promotions involves anticipating the actions of other consumers or competing companies—especially those with low demand and high perceived value.
• Example: If everyone expects a product to sell out, they buy early, thereby causing the very scarcity they feared. It’s a game of collective expectations.
4. Education and Strategic Decision-Making
• Choosing a career or university can also be seen as a strategic game: if everyone chooses the same path, the value of the degree diminishes. Game theory allows us to anticipate trends and seek alternative niches, which may hold greater value due to their rarity.
5. Politics and Voting Behavior
• Voting is not always about choosing the favorite candidate, but rather the “least unfavorable” with a viable chance of winning. Strategic voters use game theory to maximize the impact of their vote.
6. Social Media and Reputation
• Deciding what to post, when to respond, or how to interact online involves games of reputation, reciprocity, and signaling. Every action communicates something that influences others’ decisions.
🎯 In Summary
Game theory is not just for economists or strategists—it is a lens through which we can understand how decisions are made in contexts of interdependence. It helps us navigate life with greater awareness, anticipation, and strategic empathy.